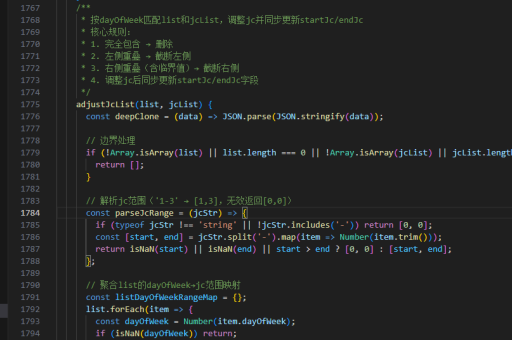
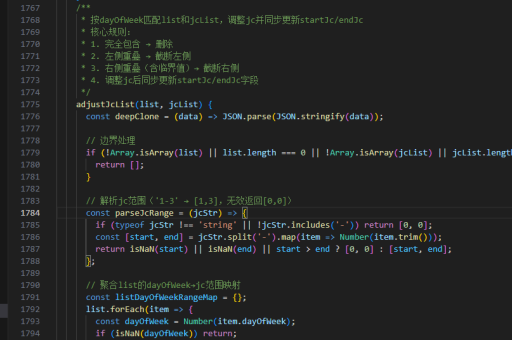
vue虚拟列表实现思路
虚拟列表的核心概念
虚拟列表是一种优化长列表渲染性能的技术,通过仅渲染可视区域内的元素减少DOM节点数量。其核心思想是动态计算可见区域的数据索引,避免全量渲染。
计算可视区域范围
监听滚动事件,根据滚动位置和容器高度计算当前可视区域的起始索引(startIndex)和结束索引(endIndex)。公式如下:
const startIndex = Math.floor(scrollTop / itemSize)
const endIndex = Math.min(
startIndex + Math.ceil(containerHeight / itemSize),
list.length - 1
)动态渲染可见项
根据计算的startIndex和endIndex截取可视数据片段,通过slice方法获取需要渲染的子集:
const visibleData = list.slice(startIndex, endIndex + 1)设置占位容器
使用padding或transform保持滚动条高度与实际列表一致。transform方案性能更优:

<div class="viewport" @scroll="handleScroll">
<div class="list-phantom" :style="{ height: totalHeight + 'px' }"></div>
<div class="list-area" :style="{ transform: `translateY(${offset}px)` }">
<div v-for="item in visibleData" :key="item.id" class="list-item">
{{ item.content }}
</div>
</div>
</div>性能优化技巧
采用Intersection Observer API替代scroll事件监听,减少主线程压力。对于动态高度项目,使用ResizeObserver监测实际高度并维护位置缓存:
const observer = new ResizeObserver(entries => {
entries.forEach(entry => {
const height = entry.contentRect.height
// 更新位置缓存
})
})动态高度处理
实现动态高度虚拟列表需要维护每个项目的位置信息(positionCache),包括顶部位置(top)、高度(height)、底部位置(bottom)。滚动时通过二分查找快速定位可视范围:
function findNearestItemIndex(position) {
let low = 0
let high = positionCache.length - 1
while (low <= high) {
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2)
if (positionCache[mid].bottom >= position) {
high = mid - 1
} else {
low = mid + 1
}
}
return low
}