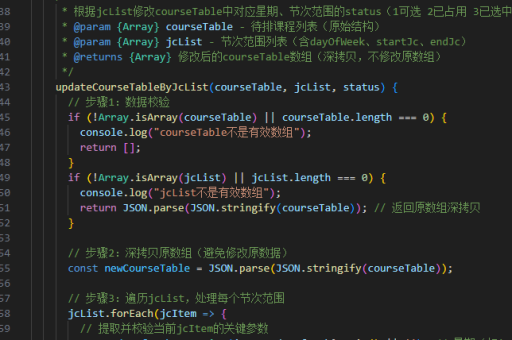
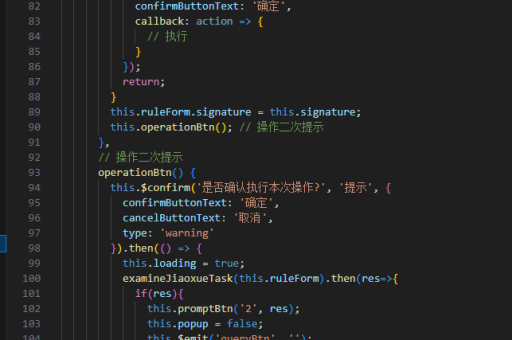
vue实现页面显示
Vue 实现页面显示的基本方法
Vue.js 是一个渐进式 JavaScript 框架,用于构建用户界面。以下是实现页面显示的核心方法:
创建 Vue 实例
通过 new Vue() 创建一个 Vue 实例,并挂载到 DOM 元素上:
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!'
}
})模板语法
使用双大括号 {{ }} 插值显示数据:
<div id="app">
{{ message }}
</div>条件渲染
v-if 指令 根据条件显示或隐藏元素:
<p v-if="seen">现在你看到我了</p>v-show 指令 通过 CSS 的 display 属性控制元素显示:
<p v-show="seen">这个元素始终存在于 DOM 中</p>列表渲染
v-for 指令 循环渲染数组或对象:

<ul>
<li v-for="item in items" :key="item.id">
{{ item.text }}
</li>
</ul>动态绑定
v-bind 动态绑定 HTML 属性:
<img v-bind:src="imageSrc">事件处理
v-on 监听 DOM 事件:
<button v-on:click="handleClick">点击我</button>计算属性和侦听器
计算属性 基于依赖缓存的计算结果:
computed: {
reversedMessage: function() {
return this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}侦听器 响应数据变化:

watch: {
message: function(newVal, oldVal) {
console.log('消息变化了')
}
}组件化开发
注册组件
Vue.component('my-component', {
template: '<div>自定义组件</div>'
})使用组件
<my-component></my-component>生命周期钩子
常用生命周期钩子:
created() {
// 实例创建完成后调用
},
mounted() {
// 实例挂载到 DOM 后调用
},
updated() {
// 数据更新导致 DOM 重新渲染后调用
},
destroyed() {
// 实例销毁后调用
}单文件组件
Vue 单文件组件 (.vue) 将模板、脚本和样式封装在一个文件中:
<template>
<div class="example">{{ msg }}</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: 'Hello world!'
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.example {
color: red;
}
</style>以上方法涵盖了 Vue 实现页面显示的主要技术点,可以根据具体需求选择合适的方式组合使用。