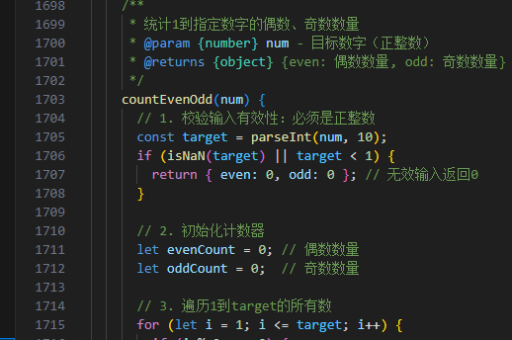
react实现请求组件
请求组件的实现方式
在React中实现请求组件通常涉及封装HTTP请求逻辑,提供统一的加载状态、错误处理和结果展示。以下是几种常见实现方法:
封装自定义Hook
使用React Hook封装请求逻辑是最现代的方式:
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function useFetch(url) {
const [data, setData] = useState(null);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true);
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
const fetchData = async () => {
try {
const response = await fetch(url);
if (!response.ok) throw new Error(response.statusText);
const json = await response.json();
setData(json);
} catch (err) {
setError(err.message);
} finally {
setLoading(false);
}
};
fetchData();
}, [url]);
return { data, loading, error };
}高阶组件方式
对于类组件或需要复用逻辑的场景可以使用高阶组件:
function withFetch(WrappedComponent, url) {
return class extends React.Component {
state = {
data: null,
loading: true,
error: null
};
componentDidMount() {
fetch(url)
.then(res => res.json())
.then(data => this.setState({ data, loading: false }))
.catch(error => this.setState({ error, loading: false }));
}
render() {
return <WrappedComponent {...this.props} {...this.state} />;
}
};
}使用Axios的请求组件
结合Axios实现更强大的请求组件:
import axios from 'axios';
function RequestComponent({ url, children }) {
const [state, setState] = useState({
data: null,
loading: true,
error: null
});
useEffect(() => {
axios.get(url)
.then(response => {
setState({
data: response.data,
loading: false,
error: null
});
})
.catch(error => {
setState({
data: null,
loading: false,
error: error.message
});
});
}, [url]);
return children(state);
}请求状态管理
对于复杂应用,建议将请求状态纳入全局状态管理:
// 使用Context API
const ApiContext = createContext();
function ApiProvider({ children }) {
const [apiState, dispatch] = useReducer(apiReducer, initialState);
const fetchData = async (url) => {
dispatch({ type: 'FETCH_START' });
try {
const response = await fetch(url);
const data = await response.json();
dispatch({ type: 'FETCH_SUCCESS', payload: data });
} catch (error) {
dispatch({ type: 'FETCH_ERROR', payload: error.message });
}
};
return (
<ApiContext.Provider value={{ ...apiState, fetchData }}>
{children}
</ApiContext.Provider>
);
}错误边界处理
为请求组件添加错误边界:
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
state = { hasError: false };
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
return { hasError: true };
}
componentDidCatch(error, info) {
console.error('Request Error:', error, info);
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
return this.props.fallback;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
// 使用方式
<ErrorBoundary fallback={<div>请求出错</div>}>
<RequestComponent url="/api/data">
{({ data }) => <div>{data}</div>}
</RequestComponent>
</ErrorBoundary>请求取消功能
实现可取消的请求:
function useCancelableFetch(url) {
const [state, setState] = useState({
data: null,
loading: true,
error: null
});
useEffect(() => {
const controller = new AbortController();
const signal = controller.signal;
fetch(url, { signal })
.then(res => res.json())
.then(data => setState({ data, loading: false, error: null }))
.catch(err => {
if (err.name !== 'AbortError') {
setState({ data: null, loading: false, error: err.message });
}
});
return () => controller.abort();
}, [url]);
return state;
}以上实现方式可根据具体需求选择或组合使用,现代React应用推荐优先使用自定义Hook方案。